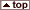2 Pulses of Hot Water Hit South American Coast in June
2 Pulses of Hot Water Hit South American Coast in June Rebounding Along the Surface Someplace South of Hawaii
Rebounding Along the Surface Someplace South of Hawaii Stimulated by Removal of Wind Pressure From the Indonesian Area
Stimulated by Removal of Wind Pressure From the Indonesian Area
| El Nino/Southern Oscillation | ||
|---|---|---|
| Section | Section | Section |
| Description | Impacts | Outlook |
 Collapse or Relaxation of Normal Persistent East-to-West Equatorial Tradewinds in Pacific
Collapse or Relaxation of Normal Persistent East-to-West Equatorial Tradewinds in Pacific Migration Westward of Large Atmospheric High Pressure Cell Over South Pacific From Tahiti to Australia
Migration Westward of Large Atmospheric High Pressure Cell Over South Pacific From Tahiti to Australia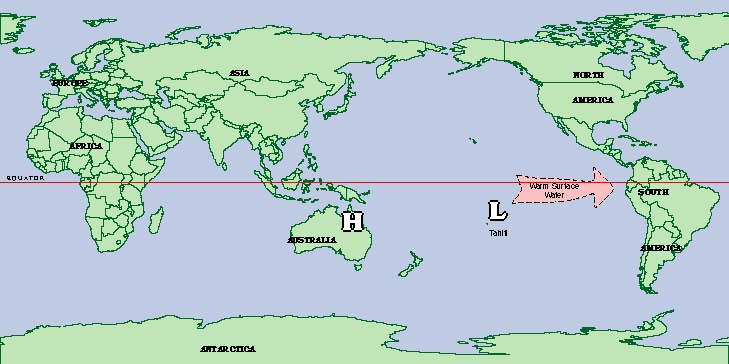
 Large Mass of Water Migrates Eastward Across Pacific Ocean from Formation Area Around Indonesian & Philippine Archipelagoes
Large Mass of Water Migrates Eastward Across Pacific Ocean from Formation Area Around Indonesian & Philippine Archipelagoes
 2 Pulses of Hot Water Hit South American Coast in June
2 Pulses of Hot Water Hit South American Coast in June Rebounding Along the Surface Someplace South of Hawaii
Rebounding Along the Surface Someplace South of Hawaii Stimulated by Removal of Wind Pressure From the Indonesian Area
Stimulated by Removal of Wind Pressure From the Indonesian Area
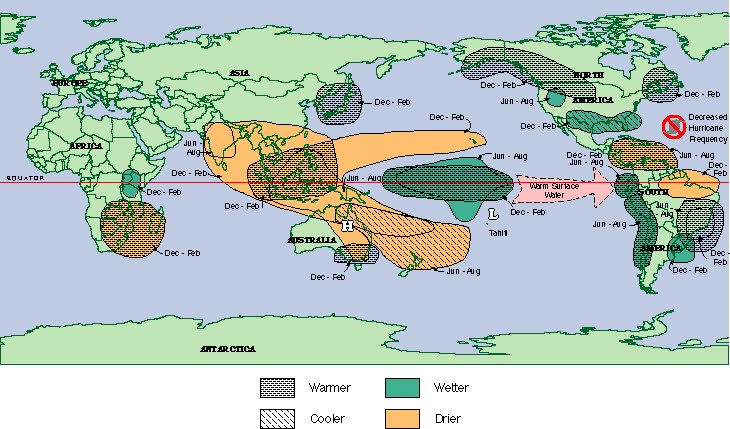
 Intense droughts in Australa, India, Indonesia, Philippines, Brazil, parts Africa, the Western Pacific Basin Islands, Central America
Intense droughts in Australa, India, Indonesia, Philippines, Brazil, parts Africa, the Western Pacific Basin Islands, Central America Milder winters in the Northeast
Milder winters in the Northeast Wet over the south from Florida to Texas
Wet over the south from Florida to Texas Alaska and NW regions of Canada and US can be abnormally warm
Alaska and NW regions of Canada and US can be abnormally warm Hurricane activity minimal in Atlantic Ocean
Hurricane activity minimal in Atlantic Ocean Rain and flooding to California, Oregon and Washington
Rain and flooding to California, Oregon and Washington
 When Large Mass of Hot Water Came to Americas
When Large Mass of Hot Water Came to Americas
 Atmosphere Reacted by Trying to Move Heat Out in 2 ways
Atmosphere Reacted by Trying to Move Heat Out in 2 ways
 Indirect Product of Two Changes in the Atmosphere
Indirect Product of Two Changes in the Atmosphere
During an El Nino Event, South Carolina can expect the following:
 Summer Rapidly Disappearing From Memories & Thermometer
Summer Rapidly Disappearing From Memories & Thermometer
 Another Part of El Nino Process Starting Up
Another Part of El Nino Process Starting Up
 Start as Moist, Warm, Tropical Jetstream
Start as Moist, Warm, Tropical Jetstream
 SC Can Expect Between 120 - 135% Normal Precipitation within 6 - 10 months of the onset of a typical El Nino event
SC Can Expect Between 120 - 135% Normal Precipitation within 6 - 10 months of the onset of a typical El Nino event Reserch on Historical Records Show 2 Worrisome Trends
Reserch on Historical Records Show 2 Worrisome Trends